The market research actor IdTechEx estimates that there will be 20 billion RFID and NFC tags in use in 2020 with a market size of approximately 6 billion USD for the passive tags alone (1). Without making too many bold assumptions, we argue that a subset of these 20 billion RFID and NFC tags will most likely demand some kind of visual feedback. We have the firm belief that the printed ultra-low-power Rdot Display is the perfect RFID and NFC Display - read more to find out why.
What are RFID and NFC?
RFID (Radio-frequency identification) and NFC (Near Field Communication) are two similar technologies that are widely used for near field wireless communication. They both use radio waves to communicate between an RFID/NFC Tag (an antenna) and an RFID/NFC Reader (a microchip for transmitting and/or receiving information). The NFC communications protocols and data exchange formats are based on RFID standards and NFC can be considered a subcategory of RFID. For the purpose of simplification, NFC will be included when using the broader term RFID.
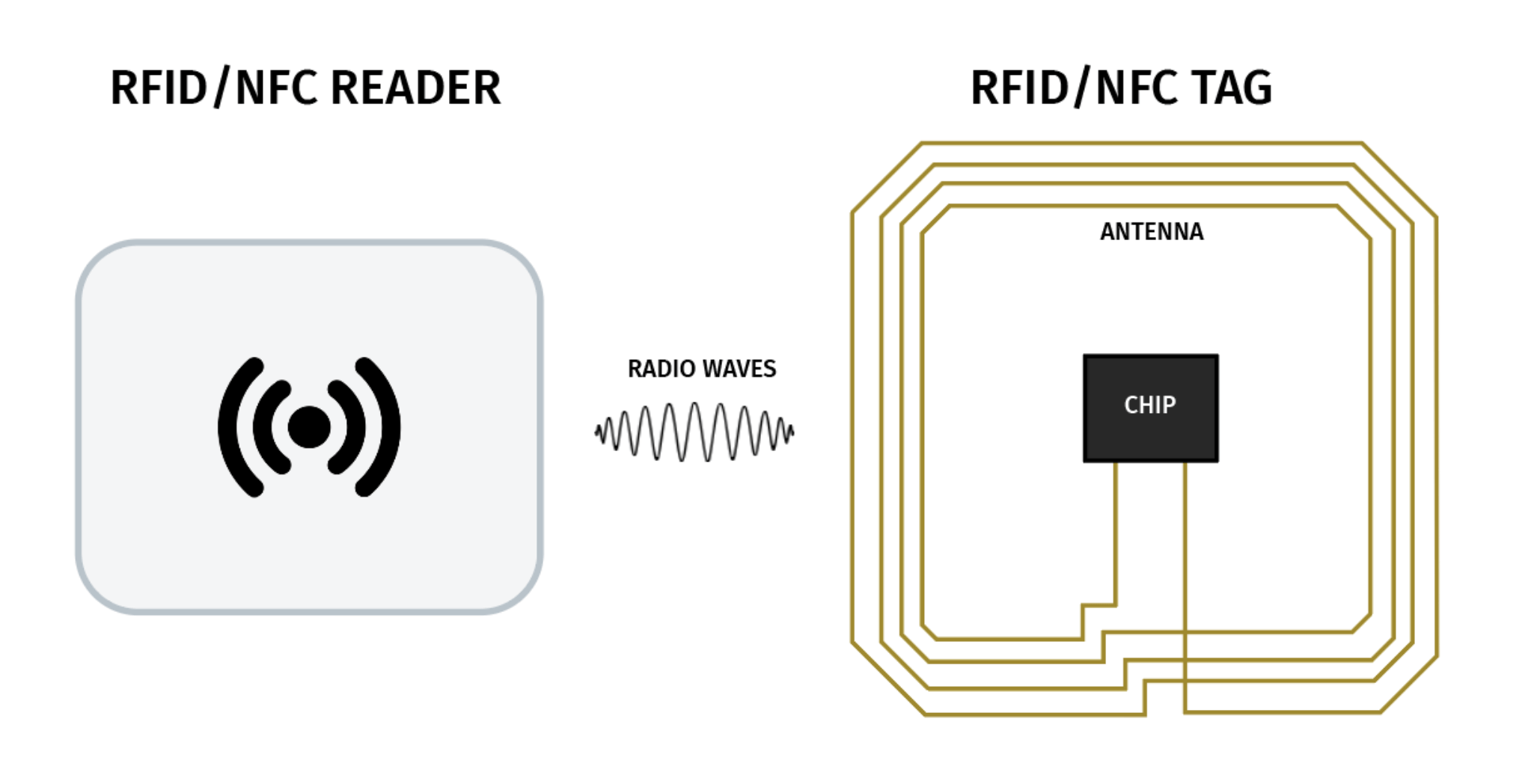
The RFID tags generally hold a memory with a storage capacity up to 8Kb and a data transfer rate of a few hundred kbps when in communication with the RFID reader. The information stored in the memory is therefore fairly limited and typically involves a unique identification string and optionally other data relevant for the specific application where the tag is implemented. Common applications for RFID tags involve logistics and supply chains, inventory management, and credit cards.
Active and Passive RFID tags
There are two main categories of RFID tags; active and passive. The active RFID tag uses an internal power source, typically a battery, to communicate with the RFID reader. The active RFID tags typically communicate across a longer distance, up to 100 meters. Passive RFID tags (including NFC tags) use no internal power source but are instead making use of external power from electromagnetic fields generated by the RFID reader. This phenomenon is commonly referred to as energy harvesting.
Why Rdot Display for integrated RFID visual feedback?
Before we get into several examples of RFID including on-device visual feedback, we'll introduce some requirements for the display solution.
Low-Cost Requirements and Mass Production
Low unit cost is an overall requirement for most of the RFID applications. The RFID tags, especially the passive chipless tags (3), has dropped significantly in cost thanks to enhanced production methods, such as dry phase patterning and printed electronics, and also the economy of scale as a result of increased adoption and new applications.
A low-cost display is required due to the cost-sensitivity. If the display is expensive, the entire purpose of implementing the RFID solution can become obsolete. Another aspect is that the display could be a nice-to-have feature and not a need-to-have feature at a system level. This fact results in an even greater need for low-cost displays.
Low-Power and Image Memory Requirements
Battery-less RFID application is likely reliant on some kind of energy harvesting solution for power supply. The transferred power should be sufficient for reading and writing data but also to activate the visual feedback. Most energy harvesting IC will transfer no more than a few mW during a short time frame. The harvested energy should also be sufficient to sustain the visual feedback for an adequate time. This typically requires a bistable or semi-bistable display that will retain the image without any power.
Flexible Design and Form Factor
Different applications demand different visual feedback. The display solution should be highly customizable to match the requirements of the specific device. Flexibility is not always a necessity, but it could in some cases add increased value and certainly also make the devices more robust as they will not crack if bent.
Summary
The Rdot Display is the only display technology on the market that can tick off all of the requirements above. Rdot Displays are the most energy-efficient for most use-cases, they are inherently flexible and highly customizable, and highly cost-effective in large volumes thanks to efficient roll-to-roll screen printing processes.
Rdot RFID Display - Use-cases and Examples
We highlight three use-cases that we believe will account for a large part of the increased adoption of RFID. All applications will benefit from an integrated on-device visual feedback solution. We propose that the Rdot Display is the best display technology for these applications and use-cases.
1. Authenticity & Security
Billions of dollars are lost each year due to counterfeited products. Anti-counterfeiting solutions will not only defeat corrupt suppliers, but it will also guarantee that the customer receives a genuine product and limits the associated risk. Some products, such as medicines, eatables, and alcoholic beverages, can pose a direct risk to consumers if they are counterfeited. Novel hardware solutions that are not possible to copy as authenticity certificates mean great opportunity to tackle this situation.

Existing solutions exist that utilize primarily QR or RFID/NFC together with a server-side validation with software. This methodsd is much easier to replicate in comparison to novel proprietary hardware.
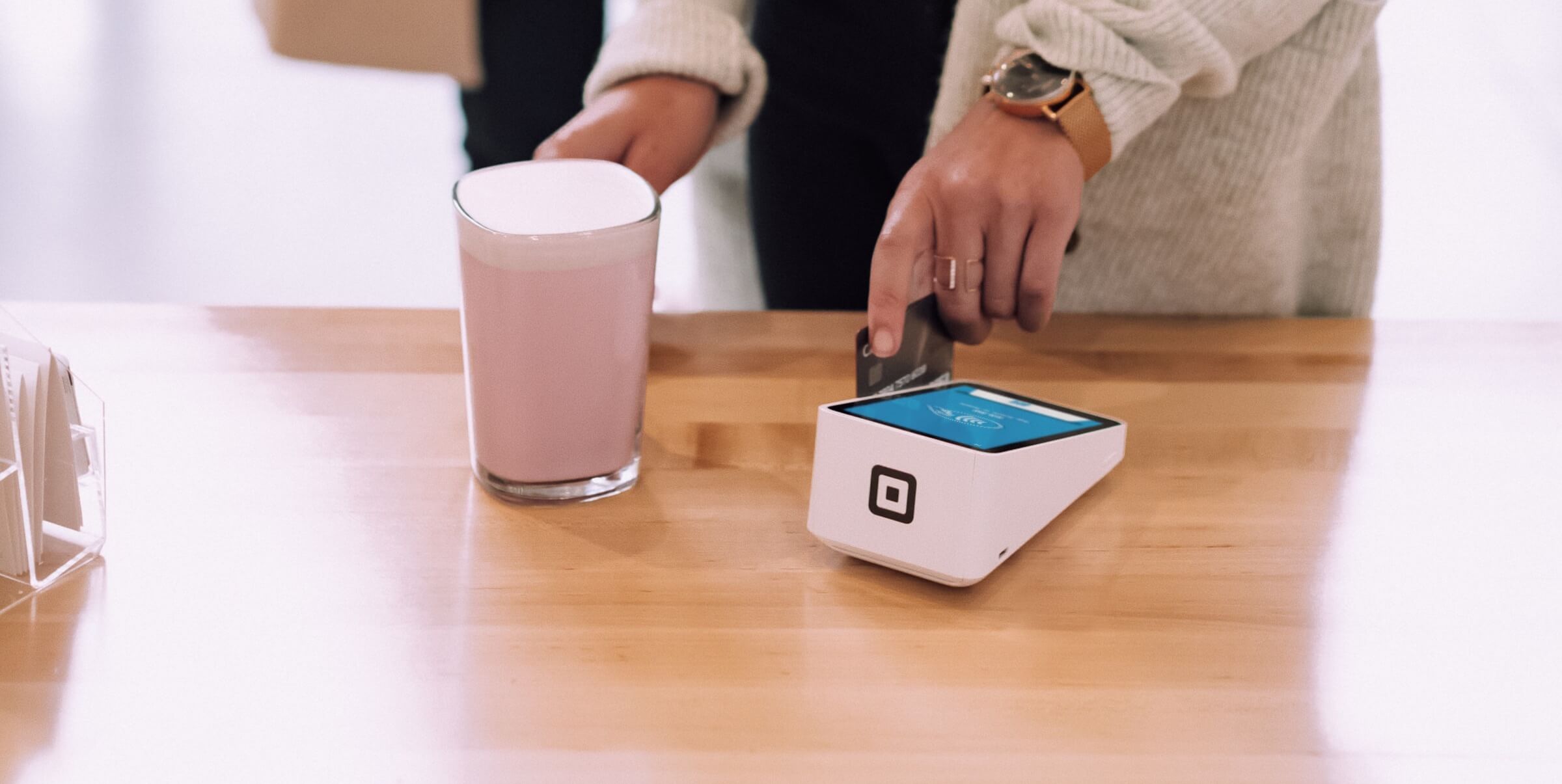
2. Contactless Payments
Contactless payment is one of the drivers for the RFID/NCF chips market. Smart cards are increasingly used, with features such as dynamic CVC/CVV codes. A contactless payment solution can be enhanced with simple visual feedback after the successful or unsuccessful purchase.

The visual feedback will improve the customer experience and value proposition from the smartcard manufacturers.
3. Event and Activity Visualization
Event and activity visualization is a broad genre of sub-applications where visual feedback for RFID can be implemented. To concretize, the use-cases can involve:
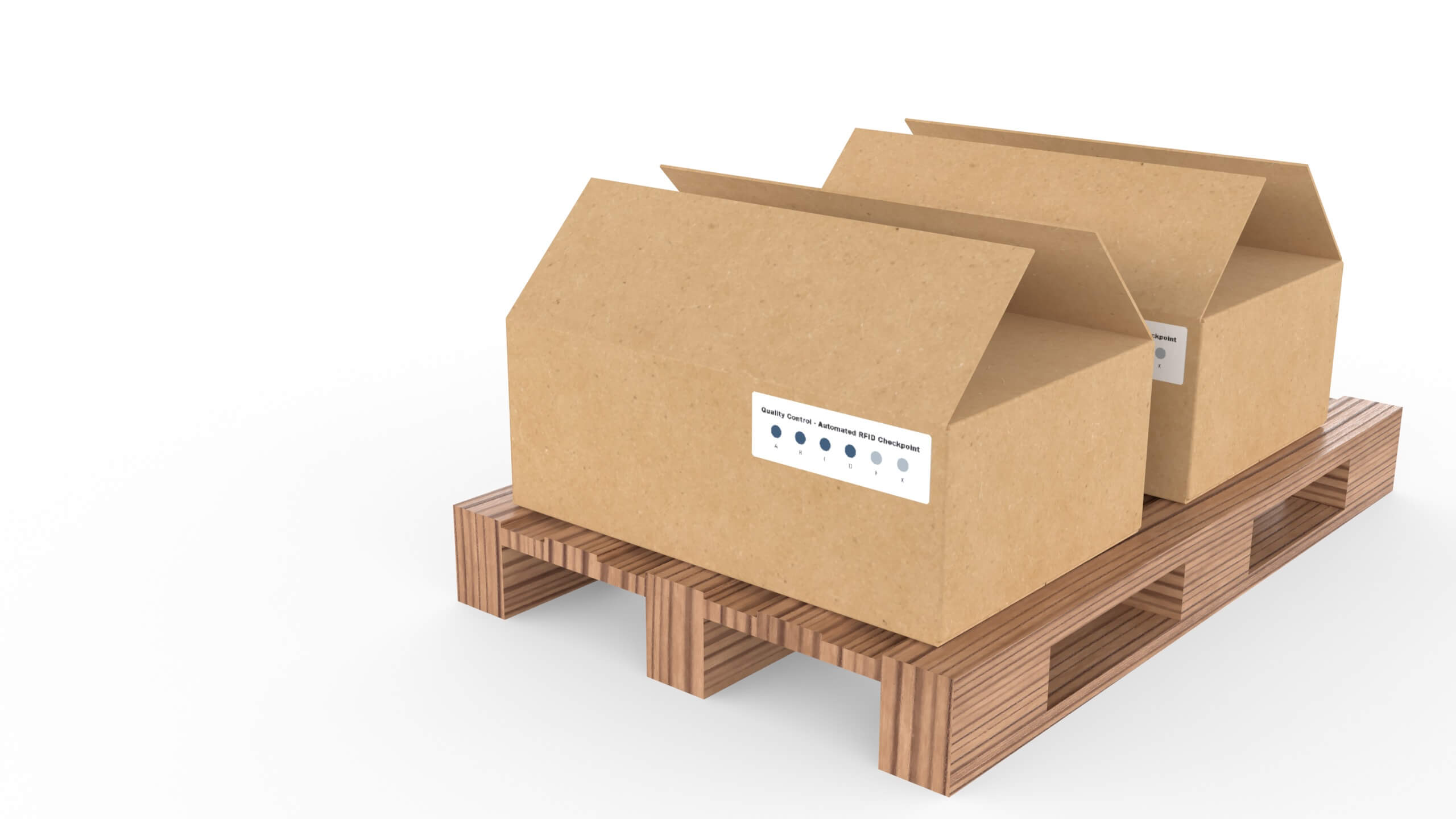
- Maintainance Tracking - the item has been monitored or served and the item should update a counter or a date indication with help of RFID and a low-power display.
- Supply chain monitoring and control - based on a triggered event, such as a new position, the device updates an irreversible progress bar to show that all necessary quality processes have been passed.
- Product Status Update - the status of the product has changed from, for instance, enabled to disabled.